Essential Guide to Prototype Machining Techniques and Benefits
In the fast-paced world of manufacturing, prototype machining has emerged as a critical component in the product development lifecycle. According to a report by the Association for Manufacturing Technology, 70% of organizations have integrated prototyping into their development processes to accelerate time-to-market and enhance product quality. The ability to quickly transform digital designs into tangible prototypes allows engineers and designers to test concepts, iterate designs, and ultimately deliver superior products that meet market demands.
Prototype machining encompasses a variety of techniques including CNC machining, additive manufacturing, and traditional methods such as turning and milling. Each method offers distinct advantages that cater to specific project requirements, whether it be speed, precision, or material versatility. The Global Market Insights report indicates that the prototype machining segment is projected to grow significantly, driven by advancements in technology and an increasing need for rapid prototyping across various industries such as aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics. This essential guide aims to explore the various prototype machining techniques, their benefits, and their impact on modern manufacturing practices, providing valuable insights for industry professionals seeking to optimize their prototyping processes.

Overview of Prototype Machining Techniques
Prototype machining is a critical step in product development, allowing engineers and designers to create functional models quickly and efficiently. Among the various techniques available, CNC machining stands out due to its precision and versatility. According to a recent industry report, CNC machining accounts for over 70% of all prototype machining processes, largely due to its ability to produce complex geometries with tight tolerances. Other techniques, such as additive manufacturing and manual machining, are also valuable depending on the specific requirements of the project. Each method has its strengths and can be selected based on the material, design complexity, and the intended application of the prototype.
Tips: When choosing a machining technique, consider the required turnaround time and budget constraints. CNC machining is often faster for complex designs, while additive manufacturing can be cost-effective for lower volumes. Additionally, it's essential to assess the material properties needed for the prototype, as this will influence the machining technique and tool selection.
Post-processing is another vital aspect of prototype machining that should not be overlooked. Techniques such as sanding, polishing, and coating can significantly enhance the functionality and aesthetics of the prototype. Industry findings indicate that nearly 40% of prototypes require some form of post-processing to meet design specifications. Ensuring that your chosen machining method allows for easy post-processing can lead to a more refined end product.
Essential Guide to Prototype Machining Techniques and Benefits
| Technique | Description | Benefits | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Machining | Computer Numerical Control machining that uses computer software to control machine tools. | High precision, repeatability, and ability to machine complex shapes. | Automotive parts, aerospace components, medical devices. |
| 3D Printing | Additive manufacturing process that creates objects layer by layer from digital files. | Rapid prototyping, design flexibility, and reduced waste. | Concept models, tooling, custom parts. |
| Laser Cutting | Using a laser to cut materials based on computer-controlled guidance. | Precision cuts, minimal material distortion, and versatility. | Sheet metal fabrication, signage, prototyping. |
| Injection Molding | A manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mold. | High volume production and cost efficiency for plastics. | Consumer products, automotive components, electronic housings. |
Types of Machining Techniques for Prototyping
When it comes to prototyping, various machining techniques play a crucial role in shaping the design and functionality of the final product. Among the most common machining methods are CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), and manual machining. CNC machining offers precision and repeatability, making it ideal for complex geometries that require tight tolerances. This technique utilizes computer-controlled tools to create parts from a digital model, ensuring high accuracy and efficiency, which significantly speeds up the prototyping process.
EDM is another specialized technique often used when traditional cutting methods are not suitable, especially for hard materials or intricate designs. By using electrical discharges to remove material, EDM can achieve fine details that other machining processes may struggle with. Manual machining, while less common in modern prototyping due to the rise of automation, still plays a vital role for quick adjustments and small-scale custom parts. Each of these techniques brings unique advantages to the prototyping phase, allowing engineers to iterate designs and refine products before mass production.
Benefits of Using Machining in Prototype Development
In the realm of prototype development, machining techniques play a crucial role in transforming initial concepts into tangible products.
One of the primary benefits of utilizing machining in this phase is the precision it offers. According to a report by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), high-precision machining can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.005 mm, which is essential for ensuring that prototype components fit and function correctly. This level of accuracy not only accelerates the development process but also reduces the likelihood of costly revisions later in the production cycle.
Furthermore, machining allows for the rapid iteration of designs, enabling engineers to test multiple variations quickly. A study published by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) indicates that leveraging advanced machining technologies can cut prototype development time by up to 30%. This efficiency is vital in today’s fast-paced market, where time-to-market can significantly influence a product's success. Additionally, machining supports the use of a variety of materials, from metals to plastics, giving designers the flexibility to choose the best material properties for their prototypes. This adaptability not only enhances the performance of the prototype but also ensures that the final product can meet customer demands effectively.
Key Considerations for Selecting Machining Methods
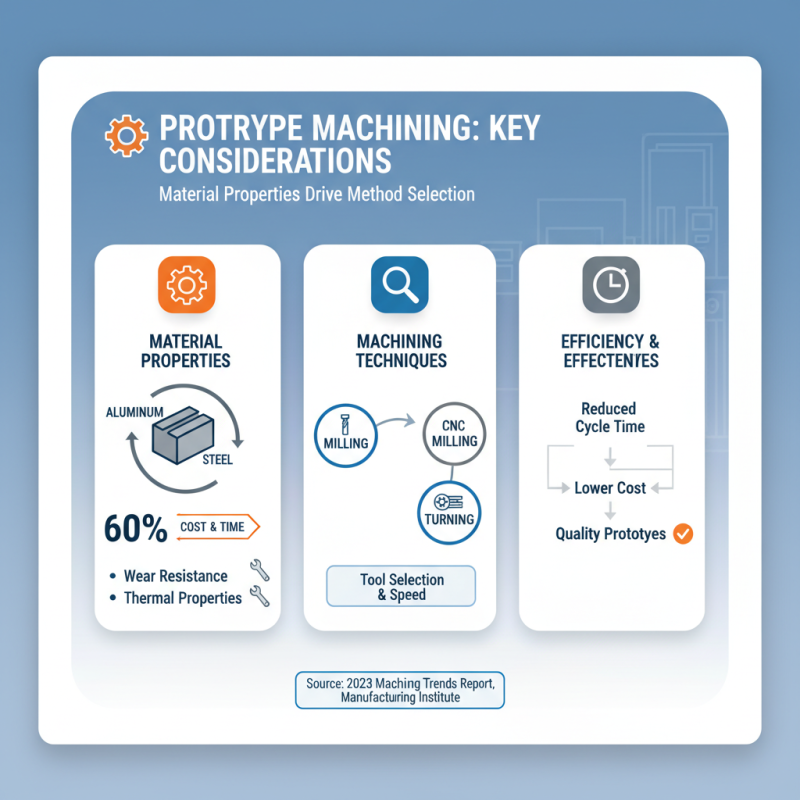
When selecting machining methods for prototypes, several key considerations are essential to ensure efficiency and effectiveness. First and foremost, the material properties play a critical role in determining the suitable machining technique. According to the 2023 Machining Trends Report by the Manufacturing Institute, nearly 60% of firms emphasize that material selection directly influences machining cost and cycle time. For instance, metals like aluminum and steel may require different machining technologies due to their distinct wear-resistance and thermal properties, thus affecting tool selection and machining speed.
Furthermore, the complexity of the prototype design significantly impacts the choice of machining method. In a survey conducted by the Precision Engineering Society, 72% of respondents indicated that intricate geometries often necessitate advanced machining techniques, such as CNC milling or wire EDM, to achieve the desired precision and surface finish. Additionally, the lead time for production is a critical consideration—quick prototyping methods like additive manufacturing may offer a faster turnaround for initial designs, but traditional machining methods are often preferred for final production runs due to their scalability and cost-effectiveness. Balancing these factors ensures a streamlined prototyping process, ultimately contributing to more successful product development cycles.
Future Trends in Prototype Machining Technologies
As the world increasingly embraces digital transformation, prototype machining technologies are evolving rapidly. One of the most significant future trends is the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into the machining process. These technologies enable precision optimization, predictive maintenance, and enhanced quality control, revolutionizing how prototypes are produced.
By analyzing data from previous machining operations, AI can help in identifying trends and inefficiencies, allowing for smarter adjustments and ultimately reducing lead times.
Another notable trend is the rise of additive manufacturing techniques alongside traditional machining methods. This hybrid approach allows for greater flexibility in design and functionality, as 3D printing can be utilized to create complex geometries that are difficult to achieve through conventional machining.
Furthermore, advancements in materials science are leading to the development of new composites and alloys that can withstand higher temperatures and stress, broadening the applications for prototyping in various industries.
As these technologies continue to evolve, their potential to streamline the prototyping process and enhance product development is becoming increasingly evident.
Related Posts
-

5 Essential Tips for Optimizing Your Prototype Machining Process to Achieve 20% Faster Production Times
-

Innovative Techniques in Prototype Machining for Faster Product Development
-

10 Ways Laser Machines Revolutionize Global Manufacturing Efficiency
-

Understanding the Innovations Behind CNC Metal Cutting Techniques
-

Exploring CNC Cutting Innovations at the 138th Canton Fair 2025 in China
-

How to Use CNC Cutting Techniques for Precision Fabrication in 2025